Are you a startup eager to boost your income and grow your business?
Think of revenue drivers as the fuel that powers your company’s engine. These drivers include what you sell, how you price your products, and the strategies you use to attract customers. By understanding and optimizing these key factors, you can ensure your business runs smoothly and efficiently, driving growth and profitability.
What is a Revenue Driver?

A revenue driver is something that directly impacts a business’s ability to make money. This can include what the business sells, its pricing strategies, and customer behavior. All these factors determine how successful the business will be in terms of making money. In short, the main goal of a revenue driver is to help the business increase its income.
Think of a business as a garden, and revenue drivers are like the elements that help it grow. The products you sell are the seeds you plant; high-demand products lead to a better harvest. Pricing is like the water you give your plants; the right amount helps them flourish.
Customer behavior is the sunlight; knowing when and where it shines helps your plants grow best. These factors together determine how successful your garden will be in producing a good harvest, with the goal of revenue drivers being to maximize growth and income.
Revenue Drivers On-Balance Sheet
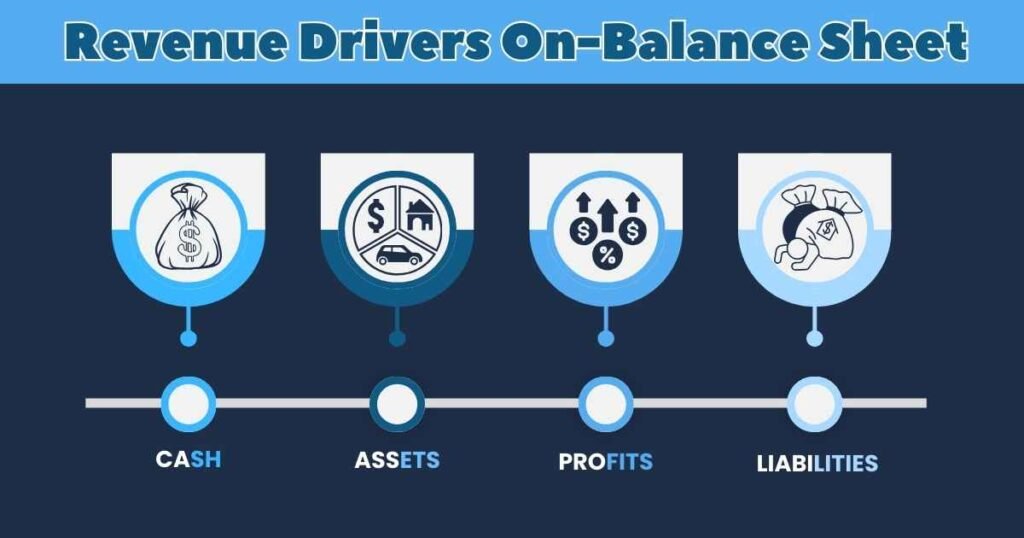
1. Cash
Companies, like people, have money in their bank accounts. When a company uses this money to buy things that make more money, we call this money a “revenue driver.”
Cash becomes a revenue driver when it helps buy things that generate more cash. For example, a company might invest in new equipment, hire more staff, or develop new products. These investments can lead to increased production, better customer service, and more sales, ultimately boosting the company’s revenue.
2. Assets
Assets are tools that help generate income. However, some assets can be quickly turned into cash, like stocks or inventory. Others, such as land and machinery, are important for producing goods and services that make money.
There are two main types of assets: those bought for potential profit, like real estate expected to increase in value, and those that directly contribute to income, like equipment used in manufacturing. In personal life, assets like homes and cars typically fall into the first category.
In business, assets can either be used to create products to sell or be sold directly to raise funds. Cash and cash equivalents are important because they can be invested to earn more money. Larger assets, like buildings and machinery, not only help produce goods but can also be sold for profit if needed.
3. Profits
When a company makes money, it can use that money to make even more money by reinvesting it back into the business. Now, let’s explain the difference between cash and profit. Cash is the actual money a company has, like the cash in your wallet. Profit is the money a company has earned, but it might not be in their wallet yet.
Some people think profit is what’s left after paying all the bills for the year. But in reality, profit doesn’t turn into cash right away. It’s often used as needed throughout the year. This is called accounts receivable and reinvestment. So, think of profit like a plant that needs time to grow and become valuable.
4. Liabilities (but not equity)
Liabilities can help us make money by letting us buy things that generate income. For instance, taking out a mortgage can allow us to purchase a property to rent out and earn rental income. Similarly, a business might take a loan to buy new equipment that increases production and revenue. Accounts payable is another type of liability, representing money we owe for supplies we’ve already received, which lets us use our cash for other immediate needs.
However, relying on liabilities can be stressful because it involves debt that must be repaid. Even so, they can be essential for businesses that don’t have enough cash flow from their usual operations to cover big purchases.
Types of Revenue Drivers
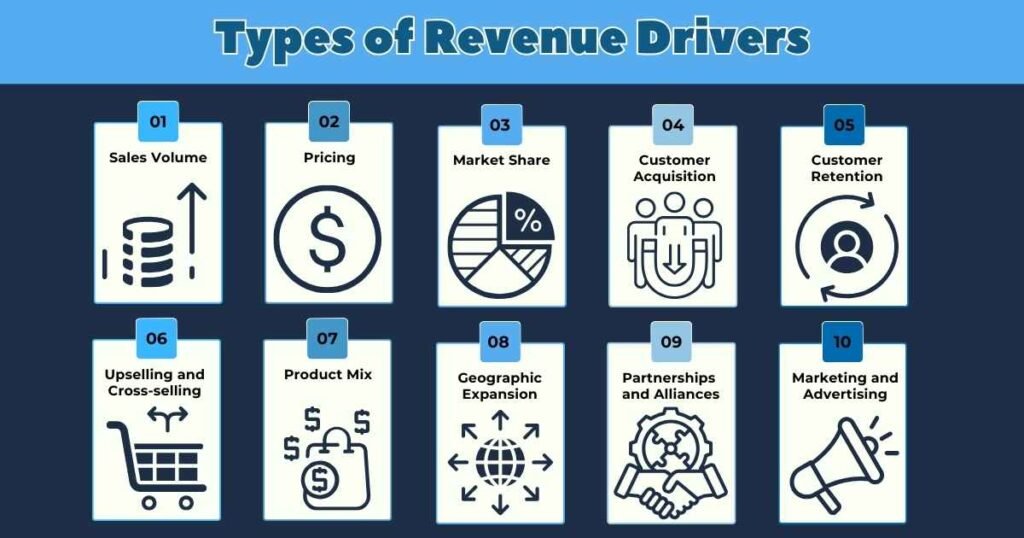
Various factors can impact a business’s financial success. Here are some common revenue drivers:
- Sales Volume: The total number of products or services sold.
- Pricing: The price at which products or services are sold.
- Market Share: The part of the total market that a business captures.
- Customer Acquisition: The number of new customers gained within a certain period.
- Customer Retention: The ability to keep existing customers and generate repeat business.
- Upselling and Cross-selling: Encouraging customers to buy additional or related products.
- Product Mix: The range and variety of products or services offered.
- Geographic Expansion: Moving into new areas or regions.
- Partnerships and Alliances: Working with other companies to reach more customers.
- Marketing and Advertising: Investing in promotional activities to increase sales.
FP&A (Financial Planning and Analysis) software helps identify the best revenue drivers and trends. Moreover, it enables businesses to find the most impactful factors, analyze trends, and take action to increase revenue growth and profitability.
Best FP&A Software for Your Revenue and Reporting Needs

Here are some FP&A software options tailored to your company’s revenue needs and reporting preferences, along with their benefits:
1. Data Analysis
Datarails is ideal for analyzing large amounts of financial and operational data. It provides strong data analysis features and easy-to-use reporting and visualization tools for advanced insights into revenue drivers.
2. Reporting and Visualization
Great for generating insightful reports and visualizations on revenue drivers is Anaplan. It excels in forecasting and budgeting, helping businesses create accurate revenue forecasts using historical data and market trends.
3. Forecasting and Budgeting
Vena Solutions is known for its powerful reporting and visualization features. It helps create accurate revenue forecasts and budgets based on historical data and market trends, offering interactive dashboards and comprehensive reports.
4. Scenario Planning
Planful is ideal for simulating different scenarios and assessing their impact on revenue drivers. It offers strong scenario planning capabilities to help businesses make informed decisions and optimize performance.
5. Trend Analysis
Prophix if recommended for tracking revenue driver performance over time and identifying patterns and trends to guide decision-making.
6. Collaboration and Communication
Workday Adaptive Planning is popular for facilitating collaboration and communication between teams, helping them share insights and align efforts to optimize revenue drivers.
Final Thoughts
Revenue drivers are key to a company’s financial success, much like gears in a money-making machine. They include sales, market share, customer relationships, and operational efficiency. Furthermore, businesses use financial tools and software to understand and manage these revenue drivers. These tools help analyze, report, and visualize important data. By using FP&A tools, businesses can gain insights, make better decisions, and optimize their revenue drivers, leading to financial growth and success.
FAQs
What are the 5 key revenue drivers?
The key revenue drivers for a business typically include sales volume, pricing strategy, customer acquisition, customer retention, and market expansion. However, these factors play an important role in determining a company’s financial success by directly impacting the amount of revenue generated.
What are the four key revenue drivers?
When considering the four key revenue drivers, businesses often focus on sales volume, pricing strategy, customer acquisition, and customer retention. Furthermore, these elements are essential for maintaining a steady revenue stream and ensuring the growth and stability of the company.
What are the key drivers of revenue forecasting?
The key drivers of revenue forecasting involve analyzing historical sales data, market trends, pricing strategies, and customer behavior. Moreover, by understanding these factors, businesses can make accurate predictions about future revenue and develop strategies to maximize their financial performance.
How to find revenue drivers?
To find revenue drivers, companies need to do detailed market research, study their sales data, and understand what their customers want and how they behave. Furthermore, this involves looking at what significantly impacts revenue growth and focusing on improving these areas for better financial results. The process might include surveys, customer feedback, competitive analysis, and using analytics tools to get deeper insights into what drives revenue.
