Revenue is all the money a business earns from activities like selling products, offering services, or making money from property it owns. It’s the first measure of a business’s financial performance. Profit is the money left after all business costs are paid.
These costs include things like salaries, rent, and materials. If a company spends more than it earns, it doesn’t make a profit. This is why businesses try to boost their earnings and keep costs down to ensure they end up with a profit.
What is Revenue?

Revenue is often called the top line because it shows up first on the income statement. It represents the money a company makes from its activities before taking out any costs.
Additionally, companies often report gross revenue and/or net revenue. Gross revenue includes all the sales a company makes before subtracting any returns or discounts. After calculating these deductions, the company reports net sales or net revenue.
It’s important to understand that net revenue doesn’t include company expenses; it simply shows the total revenue after adjusting for things that might reduce the overall amount.
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) vs. Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
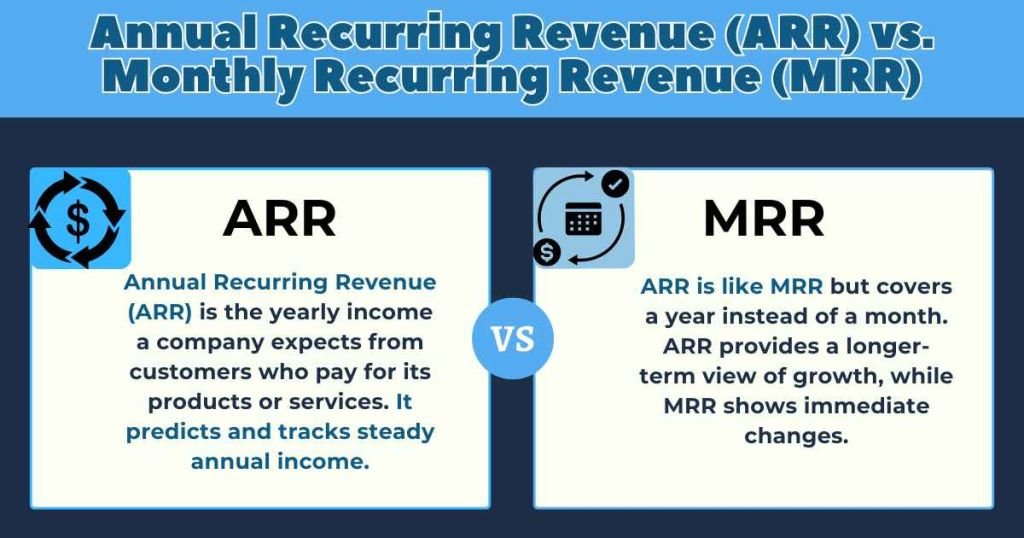
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is the money a company expects to earn every year from customers who pay for its products or services. Basically, ARR is a way to predict and track the steady income customers will bring in annually.
ARR is similar to Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), with the main difference being the time period they cover—ARR is calculated yearly, while MRR is calculated monthly. This means ARR gives a longer-term view of a company’s growth, while MRR helps see more immediate changes.
Managers use ARR to check on the company’s overall health and to understand how well long-term business strategies are working.
How to Use ARR?
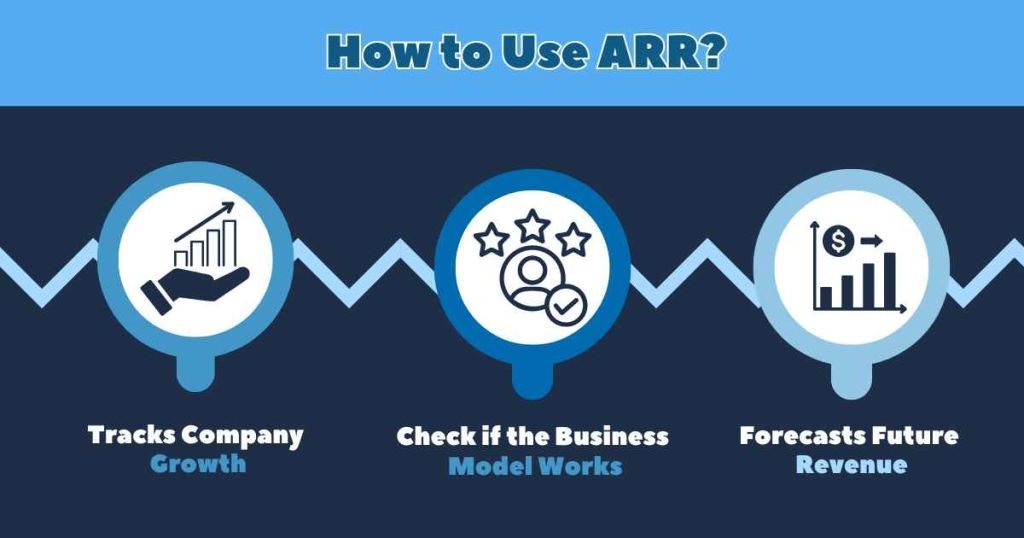
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) is extremely important for companies that use a subscription model. It acts as a key measure for several important areas within a company:
1. Tracks Company Growth
ARR is a useful tool for measuring a company’s growth. By looking at ARR from different years, a company can see how its business decisions are affecting its progress.
2. Check if the Business Model Works
Unlike total revenue, ARR only looks at money made from subscriptions. This helps a company figure out if its subscription approach is successful or not.
3. Forecasts Future Revenue
ARR is commonly used as a starting point for more complex predictions of future company revenues.
How to Calculate ARR
To calculate Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), only include regular income and exclude any one-time or variable fees.
In a simple example, ARR can be calculated from multi-year contract data.
Sure, here’s another example:
Imagine a company has two customers who each sign up for a three-year subscription costing $15,000 each. To find the company’s Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), first calculate the total contract value and then divide it by the number of years:
Total contract value = $15,000 * 2 = $30,000
ARR = $30,000 / 3 = $10,000
For multiple customers, perform this calculation for each one and then add up all the yearly figures to get the total ARR.
However, in real-world scenarios, companies often break down the total ARR into different parts. The main components of ARR include:
- ARR from new customers.
- ARR from renewals by existing customers.
- ARR from upgrades by current customers.
- ARR lost from downgrades by existing customers.
- ARR lost from customers who leave.
Breaking down the total ARR helps a company understand which customer groups most affect its ARR.
What is Profit?

Profit, also known as net income, is found at the bottom of the income statement and is often referred to as the bottom line. The income statement shows different types of profit to help analyze a company’s performance. For example, profit can be mentioned in terms of gross profit and operating profit, which are steps toward calculating the final net profit.
Gross profit is the revenue a company makes minus the cost of goods sold (COGS), which are the direct costs associated with making the products a company sells. In addition, this includes the cost of materials used in making the products and the wages paid to workers who produce them.
On the other hand, operating profit is what you get when you subtract all other fixed and variable costs related to running the business, like rent, utilities, and salaries, from the gross profit.
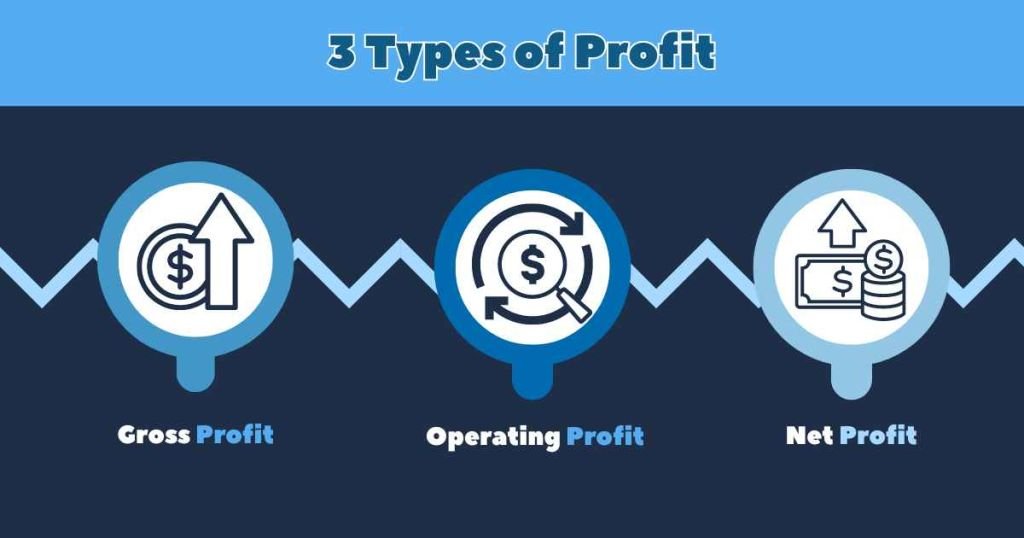
3 Types of Profit
To fully understand a business’s financial health, it is important to assess its profitability from different angles. This is why various types of profit are used to cover different revenue sources and expenses.
Here are the key types of profit you should know about:
1. Gross Profit
Gross profit is found by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from total revenue. COGS include all direct costs involved in delivering your product or service. For example, for a SaaS company, COGS might include server costs and subscription fees.
2. Operating Profit
Operating profit is found by taking away operating costs from the gross profit. Operating expenses include costs like rent, payroll, marketing, advertising, and utility bills. Operating profit, also known as net operating income, shows the essential cash flows from core business activities. It does not include interest, taxes, or income from asset sales, making it a clearer measure of business performance.
3. Net Profit
Net profit, also called the bottom line, is the actual profit after all expenses and income sources have been considered. This includes taxes, loan interest, one-time payments, and positive cash inflows from non-core activities like asset sales and investments. Net profit is usually shown on the last line of your income statement.
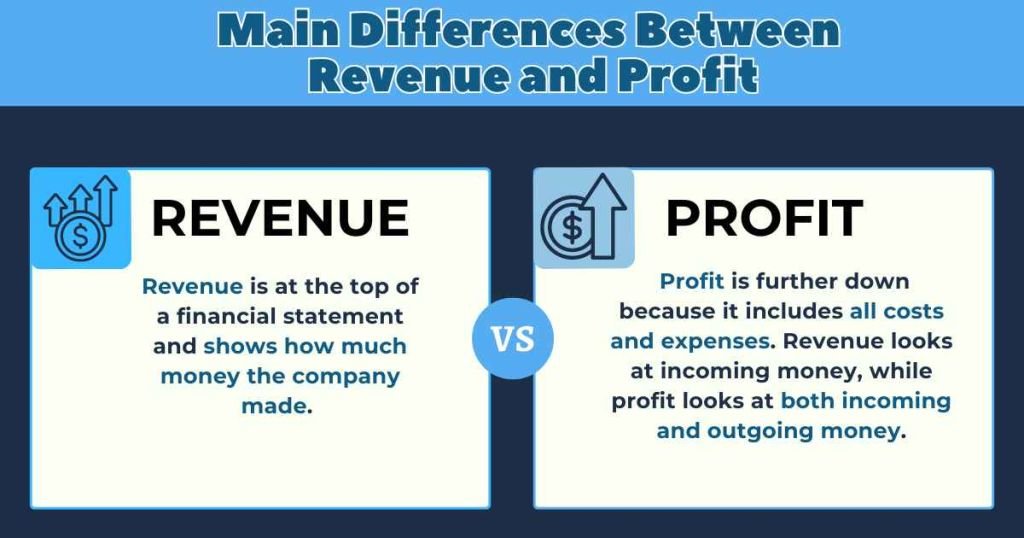
Main Differences Between Revenue and Profit
When people talk about a company’s profit, they usually mean the money left after paying all its bills, called “net income.” Sometimes, a company can make a lot of money but still end up with a loss, like Amazon.
Revenue is at the top of a financial statement and shows how much money the company made. However, profit is further down because it includes all costs and expenses. Revenue looks at incoming money, while profit looks at both incoming and outgoing money.
Companies use these numbers differently. Revenue projections help plan how much to produce and stock. Furthermore, profit helps decide where to invest. High expected profit might lead to more spending on growth, while low profit might lead to saving.
Convert Revenue into Profit
Companies start by stating their total income. Then, they end by revealing their actual earnings. In between, they perform calculations to determine the final amount.
Here’s the formula and detailed steps for finding the final number:
Net Profit = NR – COGS – Operating Expenses – Interest Expenses – Taxes
Step 1
Find out how much money you made after subtracting things like refunds that reduced your earnings.
Step 2
Determine how much it costs to make or buy the products you sell. Include costs for materials, labor, and other direct costs, but not business running expenses.
Step 3
Calculate your earnings after subtracting the costs of making or buying the products.
Step 4
Add up all the expenses for running your business, such as rent, utilities, salaries, marketing costs, and taxes. These are general business expenses, not specific product costs.
Step 5
Subtract the business running expenses from the earnings after product costs to find out your operating profit.
Step 6
Take into account any interest paid and taxes owed. These are separate from business running expenses but affect your total profit.
Step 7
Subtract the interest and taxes from your operating profit to calculate your final net income or profit.
Apple’s Revenue Breakdown for 2023
In its financial report for January 2024, Apple Inc. Shared its financial results for the year concluding on December 31, 2023. The company earned significant revenue from its various segments:
- Product Revenue: $320.5 billion from sales of iPhones, Macs, iPads, and other hardware.
- Services Revenue: $73.8 billion from services such as Apple Music, Apple TV+, iCloud, and the App Store.
These figures are adjusted for returns and allowances but primarily reflect the gross revenue before any deductions for costs or expenses. Combining these, Apple’s total revenue for 2023 was $394.3 billion.
Costs and Expenses
To understand Apple’s profitability, we need to examine its expenses for the year:
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This includes the costs of manufacturing and sourcing the products Apple sells. In 2023, this amounted to $204.3 billion.
- Operating Expenses: These are the expenses related to running the business, such as research and development, marketing, and administrative costs. For 2023, Apple’s operating expenses were $85.7 billion.
- Interest Expenses: Apple’s financial reports indicate minimal interest expenses due to its strong cash position. For simplicity, we assume it to be $0.
- Taxes: Apple paid $35.1 billion in taxes for the year.
Apple’s Net Profit for 2023
Now, let’s calculate Apple’s net profit for 2023 using the information provided:
- Net Revenue (Total Revenue): $394.3 billion
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $204.3 billion
- Operating Expenses: $85.7 billion
- Interest Expenses: $0
- Taxes: $35.1 billion
Net Profit = Net Revenue – COGS – Operating Expenses – Interest Expenses – Taxes
= $394.3 billion – $204.3 billion – $85.7 billion – $0 – $35.1 billion
= $394.3 billion – $325.1 billion
= $69.2 billion
In 2023, Apple Inc. generated a net profit of $69.2 billion, demonstrating effective cost management and strong revenue growth. Unlike Amazon in 2022, Apple achieved significant revenue and substantial profits, highlighting its operational efficiency.
A company’s financial health depends not just on revenue but also on managing expenses and generating profits. Apple’s strong performance in 2023 reflects its strategic management and competitive position in the technology market.
Final Thoughts
Knowing the difference between revenue and profit is key to judging a company’s financial health. Moreover, revenue is the money a company makes before taking out expenses, while profit is what’s left after paying all costs. This difference is important because it shows the real financial state of the company.
FAQs
What is revenue?
Revenue is the total money a company earns from its business activities, like selling products or services, before subtracting any expenses. Moreover, it’s often called “gross income” or “sales.”
What is profit?
Profit, or net income, is the money a company has left after it deducts all expenses from its revenue. Additionally, it’s what remains after the company pays costs like salaries, utilities, and taxes.
Why is it important to understand the difference between revenue and profit?
Knowing the difference between revenue and profit is key to assessing a company’s financial health. Furthermore,revenue shows sales performance, while profit indicates how well the company manages costs and earns money.
Is it possible for a company to have high revenue but low profit?
Yes, a company can have high revenue but low profit if its costs are high. Moreover, even with strong sales, high expenses like manufacturing, salaries, or marketing can greatly reduce profit. This shows the importance of controlling costs, not just driving sales.
